HydroMet Data Management
The Hydrology Wing of IDRB being one of the core components of the department which is responsible for collection, validation and distribution of all the water-related historic and real-time data of the water resources of the state. For this, a number of gauging stations have been installed in the rivers of the State since the inception of the Department and the data collection and the related works are presently entrusted with the Field Studies Circle, Thrissur.
The important functions of this wing are:
- Collection, tabulation and processing of daily reservoir level and storage volumes from the various completed irrigation projects.
- Flood discharge assessment of Irrigation structures, Peak flood estimation and Water Balance studies of river basins.
- Preparation of comments related to State Water Policy, National Water Policy.
- Preparation of State-Specific Action Plan under National Water Mission
- Implementation of the National Hydrology Project
- Publication of Surface Water Year Book for each year incorporating river gauge and rain gauge data in four volumes
HYDROLOGICAL DATA
Without accurate measurements, there can be no understanding of the routes taken within the water cycle. Long-term monitoring of hydrologic systems and archiving the data thus collected is essential for understanding the behaviour of water resources.
The various hydrological data being collected and managed by the department include:
- Streamflow/discharge data
- Water levels
Streamflow/Discharge data:
One of the basic parameters for understanding the behaviour of a water body is to study its nature of the flow. Even though the cross-section at a point does not vary drastically, it is the velocity of water that determines its potential to affect the surrounding ecosystem. Various methods and instruments are being used by the department for velocity measurement:
- Current Meter
- Float
- Acoustic Doppler Current Profiler (ADCP)
Current Meter

Cup type Current Meter
One method that has been used for measuring discharge is the mechanical current-meter method. In this method, the stream channel cross-section is divided into numerous vertical subsections. In each subsection, the area is obtained by measuring the width and depth of the subsection, and the water velocity is determined using a current meter. The discharge in each subsection is computed by multiplying the subsection area by the measured velocity. The total discharge is then computed by summing the discharge of each subsection.
The current meter can be deployed using Bank operated Cableways, Bridge Outfit or Boat Outfit.
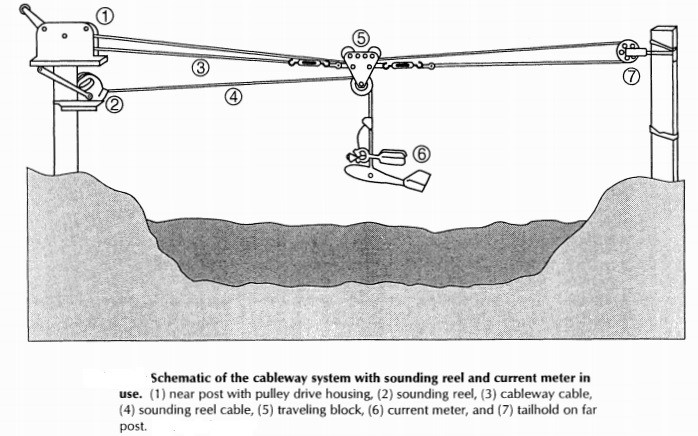
Bank operated Cableways

Bridge-outfit
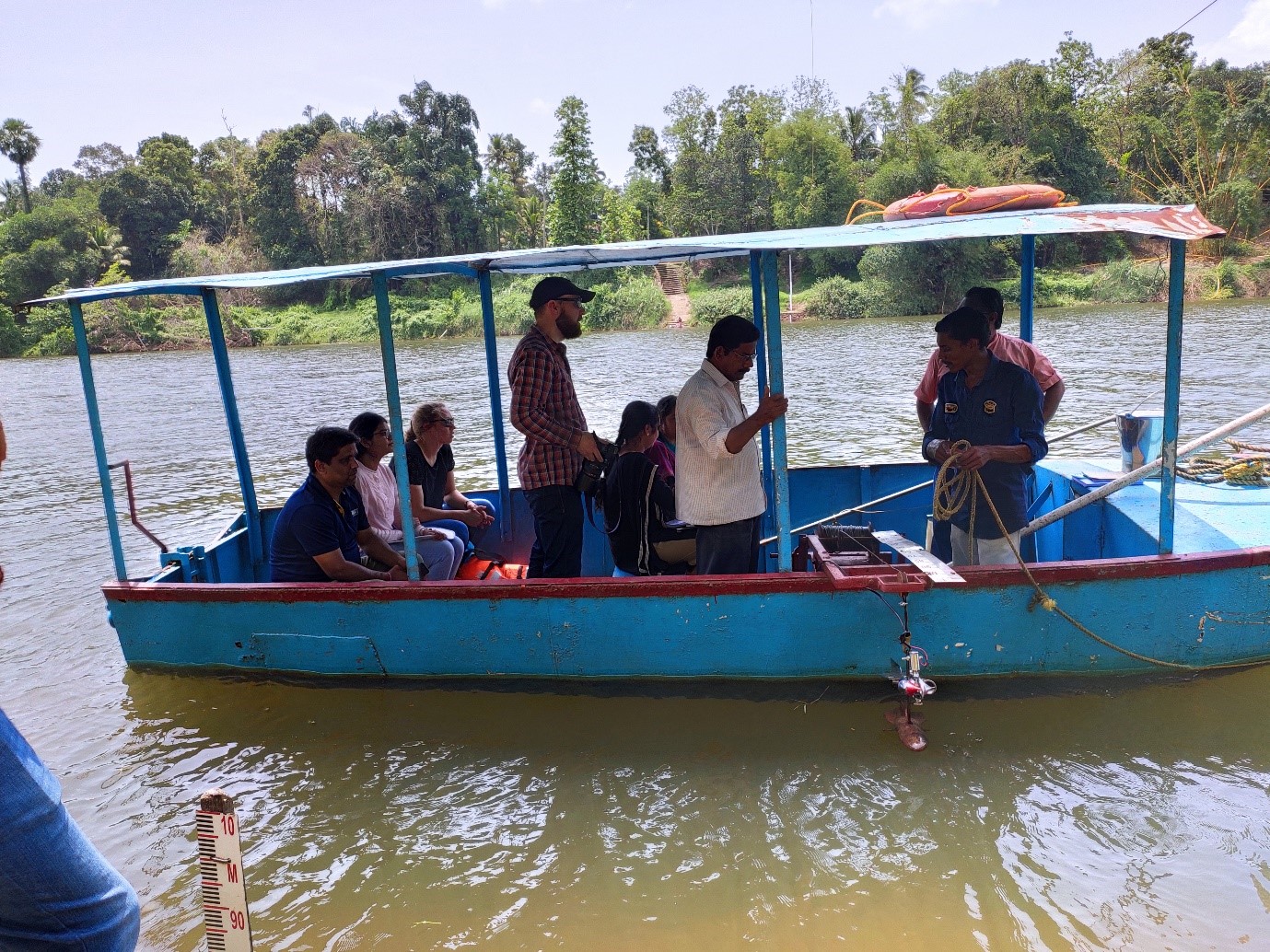

Boat Outfit
Float Method
A fairly simple method for measuring flow rate through an open channel is the Float method. Although not as accurate as a measuring device such as a flume or a flow probe, the float method can provide an educated estimate.
Briefly put, this method involves measuring the surface velocity of the water with a floating object and then multiplying this velocity by the width and average depth of the channel.
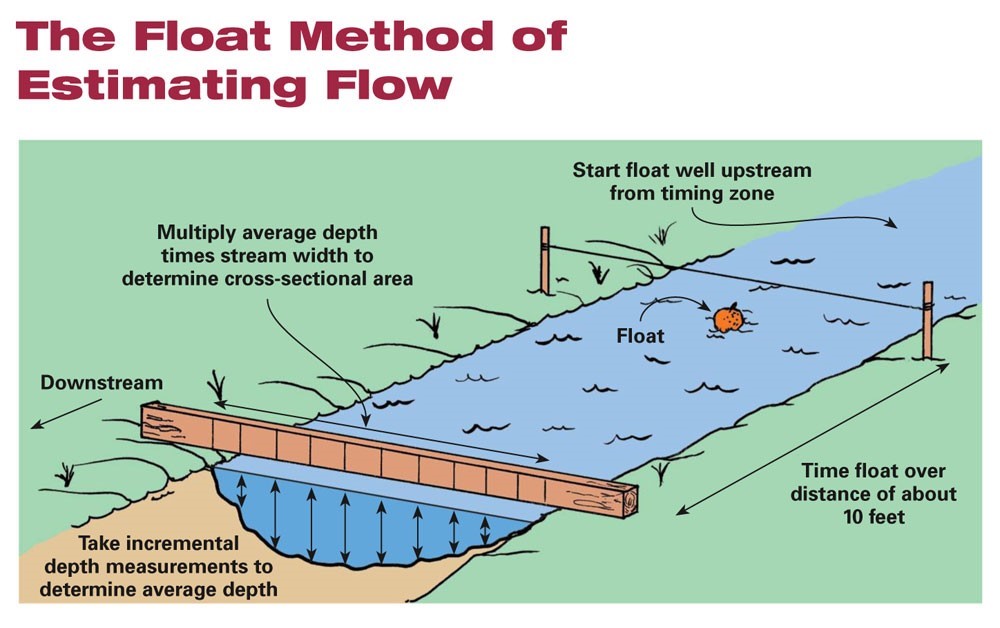
Float Method
Acoustic Doppler Current Profiler
An Acoustic Doppler Current Profiler (ADCP) is the instrument to measure how fast water is moving across an entire water column. The instrument can also be mounted on a boat to take constant current measurements as the boats move. In very deep areas, they can be lowered on a cable from the surface.
Water Levels:
Water levels are being collected regularly for studying the effect of tidal variations as well as for monitoring the levels of water bodies during floods for effective flood management and preparedness. The common methods followed for water level recording are
- Staff gauge – Manual Method
- Radar Level Sensor – Automatic Method
Staff Gauge:
A calibrated scale which is used to provide a visual indication of liquid level. When used on an inclined or sloped surface, a staff gauge is usually calibrated so that the indicated level is the true vertical level.
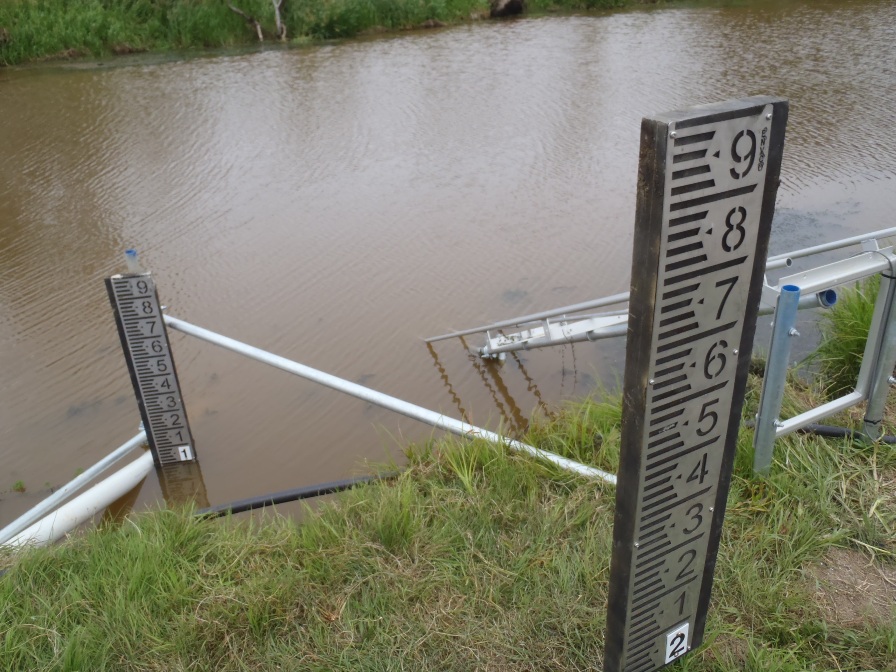

Staff Gauge
Radar Level Sensor:
A Radar Level Sensor is an instrument for measuring the height of water and converting it to an electrical signal. The water level signal output can then be utilised by other instrumentation to display, monitor, log or control the water level.
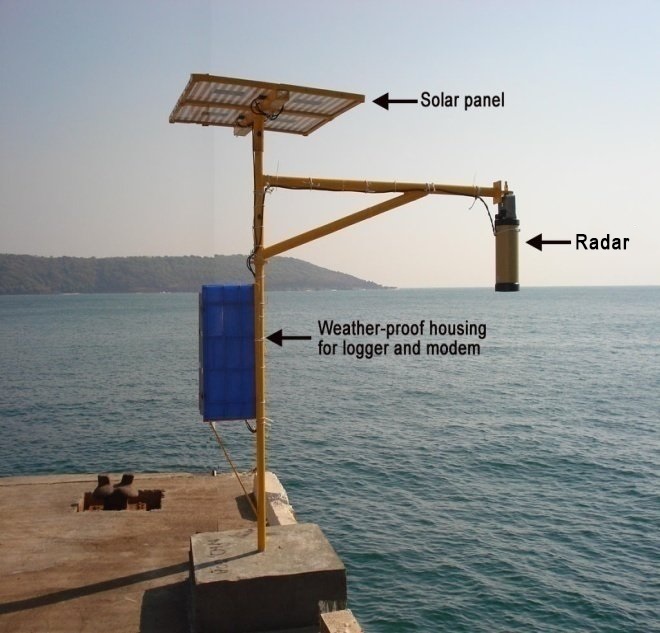

Radar Level Sensor
METEOROLOGICAL DATA
Meteorology is the scientific study of the atmosphere that focuses on weather processes and forecasting. The application of meteorology extends from weather forecasting, the study of climate change, model studies, yield potential of crops etc.
Meteorological data is collected by the department consists of physical parameters including precipitation, temperature, humidity, wind direction, wind speed, sunshine, evaporation etc.
The Meteorological Gauging Stations established by the department throughout the state can be mainly classified into two:
- Rain Gauges
- Climatic Stations
Rain Gauge:
Rain gauge is a meteorological instrument used for determining the depth of precipitation (usually in mm) that occurs over a unit area (usually one-metre square) and thus measuring rainfall amount.
Rain Gauges are of two types: Non-Recording and Recording type Rain Gauges. The common type of Non-Recording Rain Gauge is a Standard Rain Gauge, also known as the Symons Rain Gauge. Recording type of Rain Gauges used by the department include Autographic Rain Gauge (ARG) and Tipping Bucket Rain Gauge (TBRG)
Standard Rain Gauge / Symons Rain Gauge
Standard Rain Gauge/Symons Rain Gauge is a type of Non-recording rain gauge used in India. It consists of a cylindrical glass bottle which collects the rainwater through a funnel on top. The water collected is then poured into a measuring jar, which gives the cumulated rainfall for the day. This rainfall is measured at 8:30 AM every day.
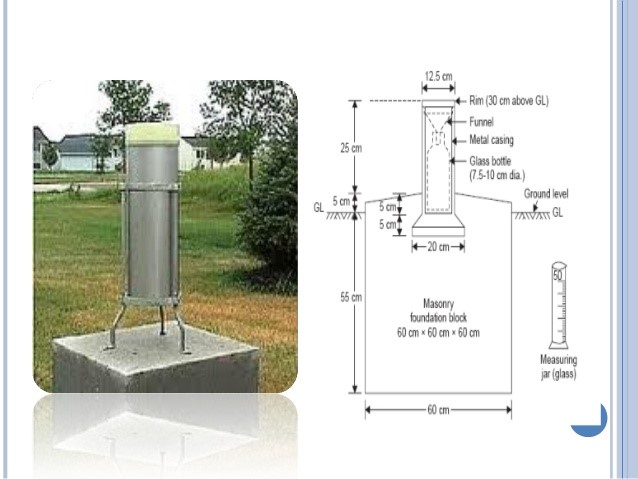
Standard Rain Gauge
Autographic Rain Gauge
Autographic Rain Gauge consists of a recording chart, which is mounted on a drum which is driven by clockwork and typically rotates round a vertical axis once per day. The rainwater in a collector displaces a float so that a marking pen attached to the float makes a continuous trace on the paper over a period of 24 hours. This type of Rain Gauges provides an exact idea of the rainfall intensity and duration at any point in time.
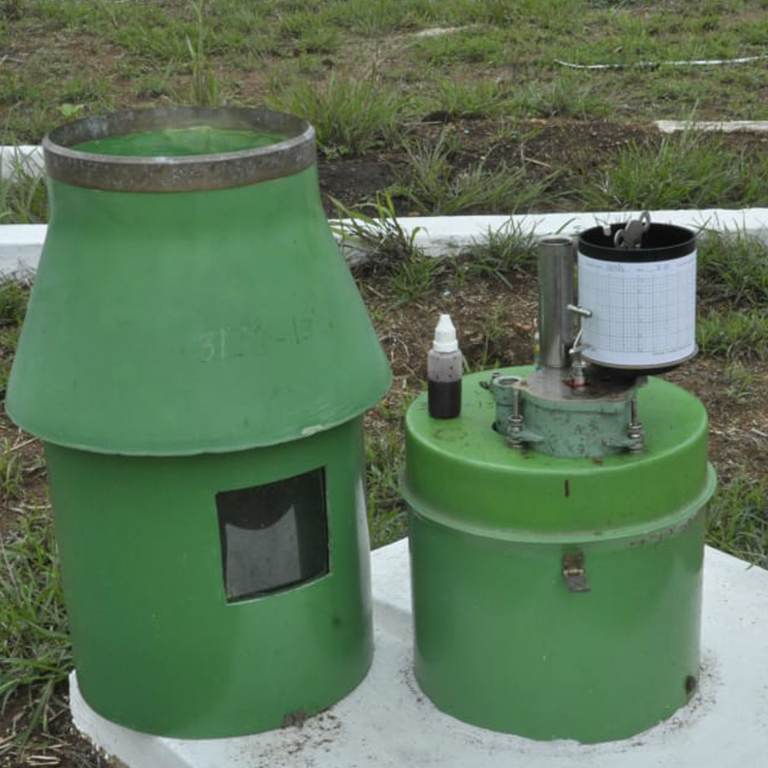

Autographic Rain Gauge
The Tipping Bucket Rain Gauge consists of a funnel that collects and channels the precipitation into a small seesaw-like container. After a pre-set amount of precipitation falls, the lever tips, dumping the collected water and sending an electrical signal.
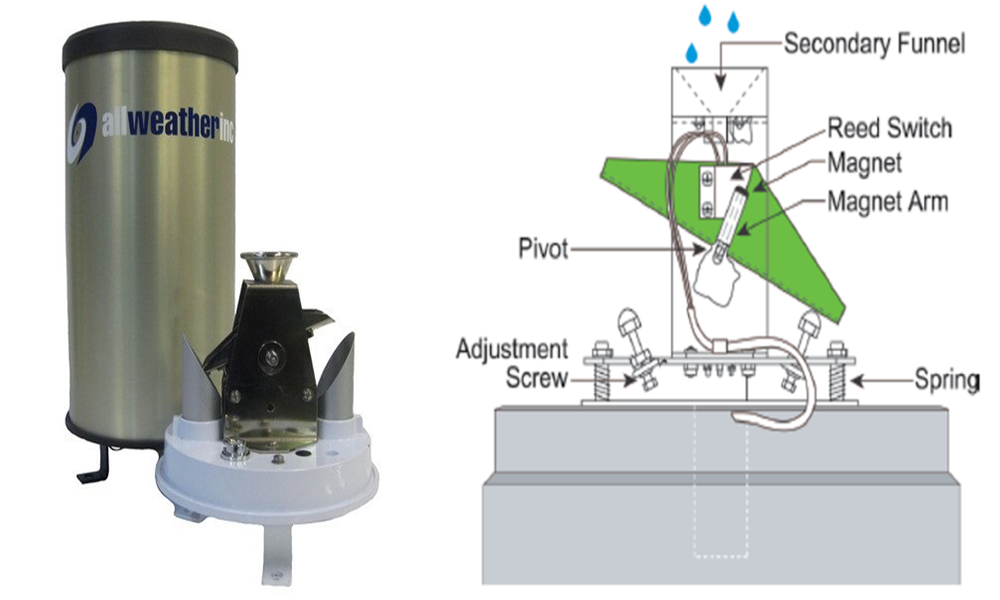
Tipping Bucket Rain Gauge
Climatic Stations:
A climatic station is a facility with instruments and equipment for measuring atmospheric conditions to provide information for weather forecasts and to study the weather and climate. The measurements taken include temperature, atmospheric pressure, evaporation, humidity, wind speed, wind direction, sunshine, and precipitation amounts.
Two types of Climatic Stations are being used by the department for meteorological data collection:
- Full Climatic Station (FCS)
- Automatic Weather Station (AWS)
Full Climatic Station (FCS):
Full Climatic Stations are manually observed stations that collect data for each parameter. The instruments used for the same includes:
Temperature
The Dry-Bulb Temperature (DBT) is the temperature of air measured by a thermometer freely exposed to the air but shielded from radiation and moisture. DBT is the temperature that is usually thought of as air temperature, and it is the true thermodynamic temperature. It indicates the amount of heat in the air and is directly proportional to the mean kinetic energy of the air molecules. Temperature is usually measured in degrees Celsius (°C).

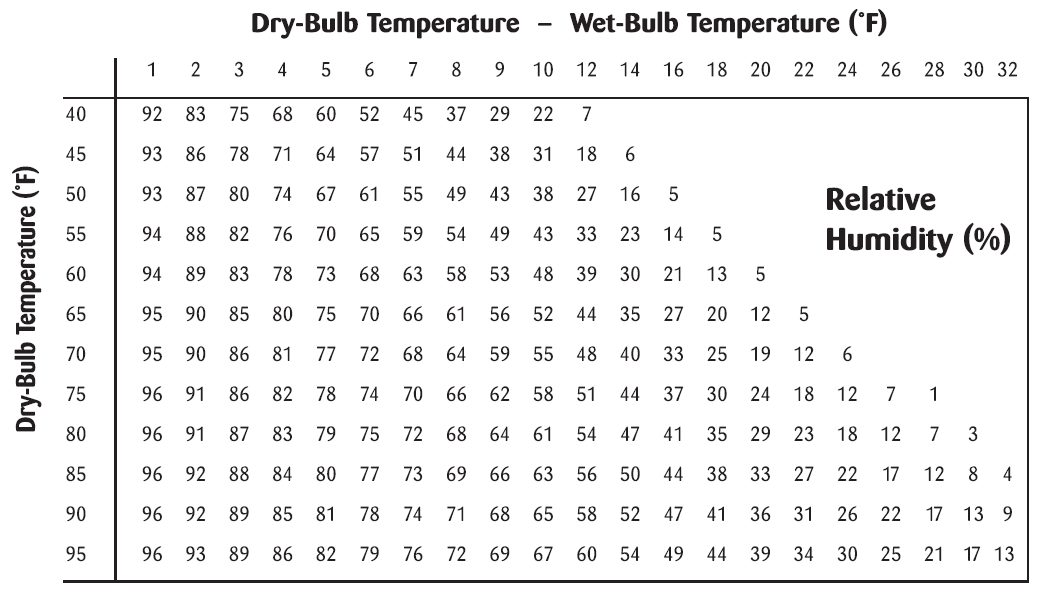
The Wet-Bulb Temperature (WBT) is the temperature read by a thermometer covered in water-soaked cloth (wet-bulb thermometer) over which air is passed. At 100% relative humidity, the wet-bulb temperature is equal to the air temperature (dry-bulb temperature) and it is lower at lower humidity. A wet-bulb thermometer indicates a temperature close to the true (thermodynamic) wet-bulb temperature. The wet-bulb temperature is the lowest temperature that can be reached under current ambient conditions by the evaporation of water only.
Relative humidity can be found by subtracting the temperature on the wet-bulb thermometer from the temperature on the dry-bulb thermometer and using a relative humidity chart.
Wind Velocity and Direction
An anemometer is a device used for measuring wind speed and direction. The term is derived from the Greek word anemos, which means wind, and is used to describe any wind speed instrument used in meteorology
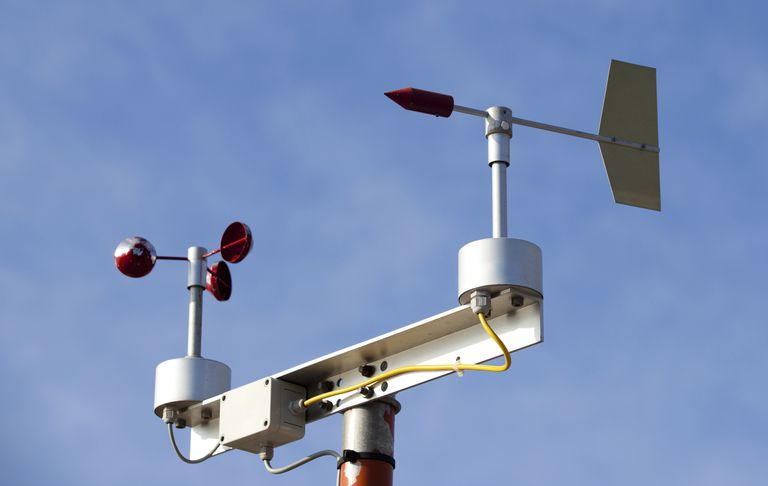

Anemometer
Sunshine
A sunshine recorder is a device that records the amount of sunshine at a given location or region at any time. The results provide information about the weather and climate as well as the temperature of a geographical area. This information is useful in meteorology, science, agriculture, tourism, and other fields. It has also been called a heliograph.
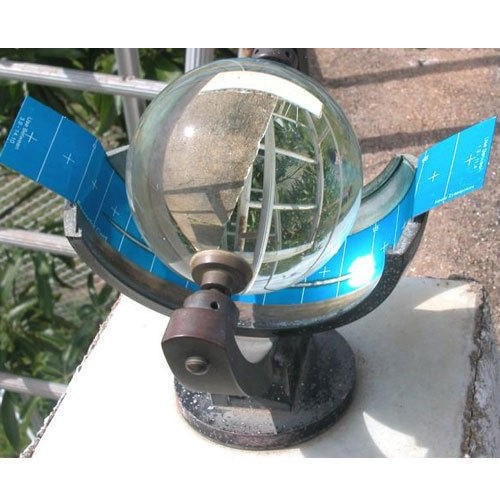

Sunshine Recorder
Evaporation
Pan evaporation is a measurement that combines or integrates the effects of several climate elements like temperature, humidity, rain fall, drought dispersion, solar radiation, and wind. Evaporation is greatest on hot, windy, dry, sunny days; and is greatly reduced when clouds block the sun and when air is cool, calm, and humid. Pan evaporation measurements enable farmers and ranchers to understand how much water their crops will need.
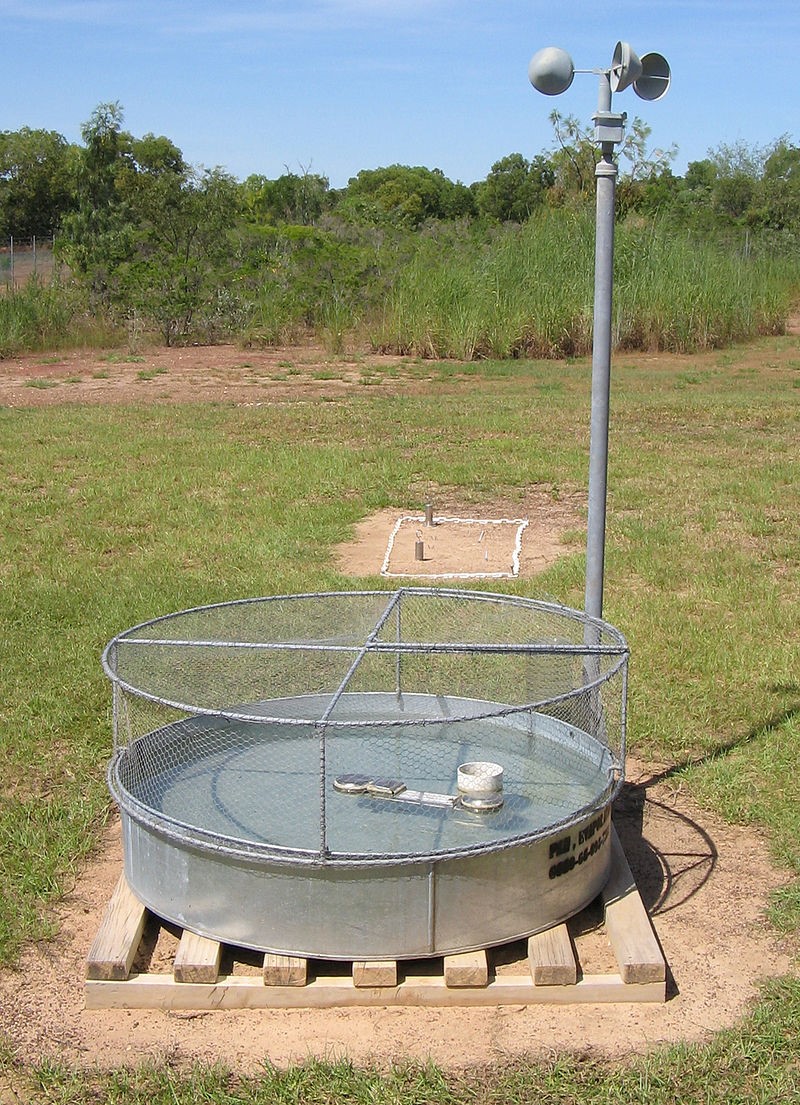

Pan Evaporimeter
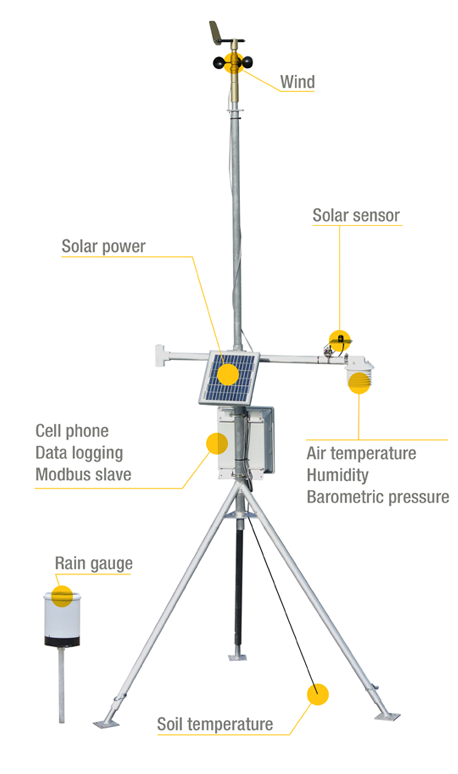
Automatic Weather Station
An Automatic Weather Station (AWS) is defined as a facility that automatically transmits or records observations obtained from measuring instruments. In an AWS, the measurements of meteorological elements are converted into electrical signals through sensors. The signals are then processed and transformed into meteorological data. The resulting information is finally transmitted the by wire or radio or automatically stored it on a recording medium. An AWS will typically consist of a weather-proof enclosure containing the data logger, rechargeable battery, telemetry (optional) and the meteorological sensors with an attached solar panel or wind turbine and mounted upon a mast.